Whitepaper Volume 3
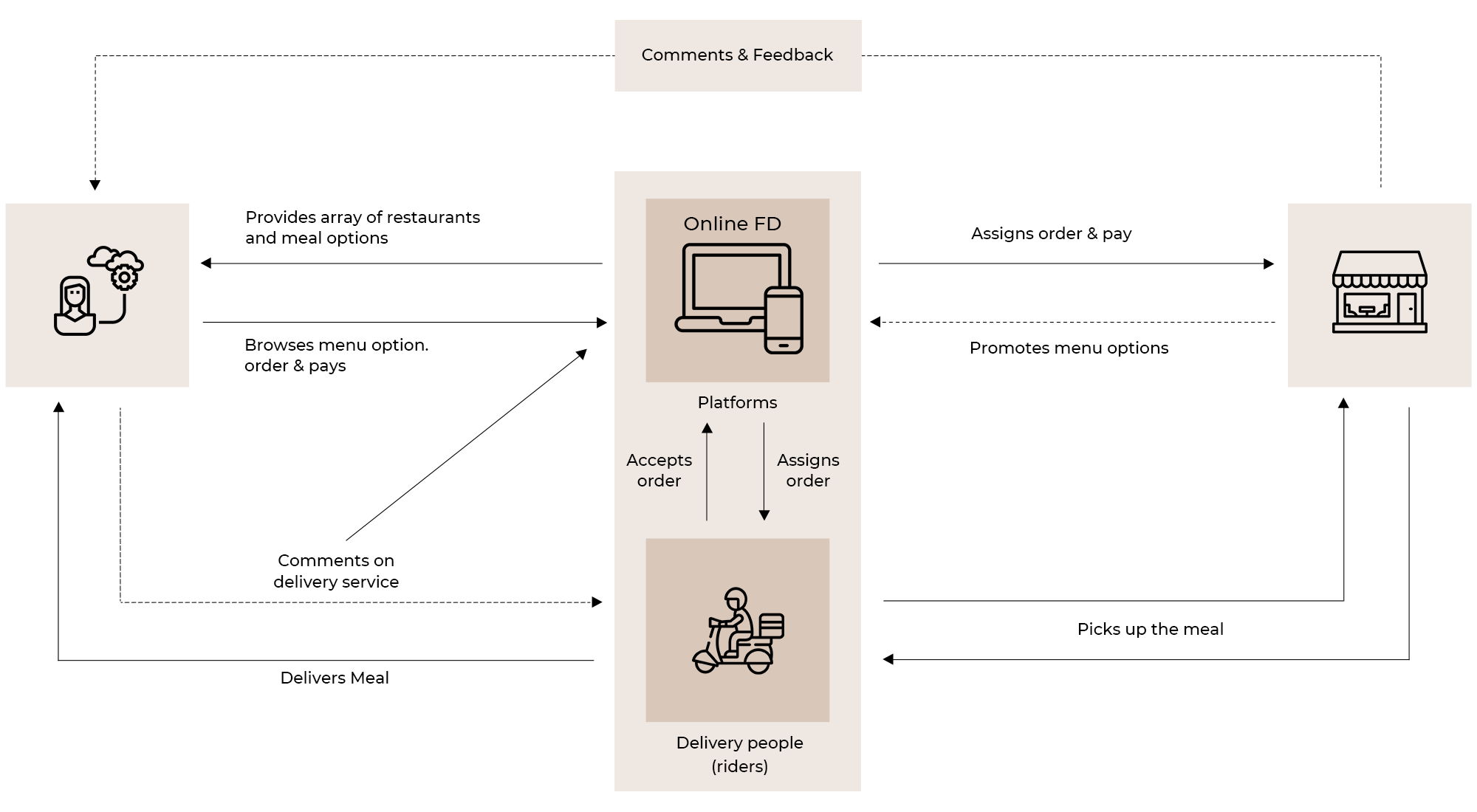
Now that awareness with respect to the components, factors, parameters, and their impact on the online food value chain are clearly defined in the discussions above, we can look into the different challenges that limit the efficiency of these value chains.
Different processes and situations cripple the food service industry in terms of ROI and profits. These challenges push the food business owners to limits in trying to maintain basic cash flow required for running the business.
Understanding how to deal with these costs and expenses while delivering the same or even better quality and service, at competitively low prices, is the actual challenge being faced by the food delivery industry today. A deep dive into these issues can contribute to coming up with solutions that might help resolve the pertaining load on the online food businesses.
Our everyday lives revolve around generating the right balance of what we earn, how we spend it, and how much we put away for a rainy day. Businesses operate and function on a similar thought. Despite trying times across the world, food service for those in need and those who had at least something to celebrate, never stopped.
Resilient services despite the pandemic by the online food industry kept the value chain going:
- Improvising on the supply chain due to restricted movements – bringing up the click and collect option
- Extending service hours with online portals and more delivery staff on-board
- Introducing direct farmer to consumer platforms for easy reach and demand generation
- Increasing the transparency around food orders placed online via tracking and feedback features
Online food ordering and delivery became one of the most common things happening around households. A casual browse through a mobile application today facilitates food delivery at the doorstep. To the world, technology has added immense convenience to the whole process, made virtual interactions easier, and enabled online processes to be automated. But what is not being observed is the imbalance in the input and the output.
With ways in which service providers are innovating offerings so as to bring online food ordering as close as possible to reality, the customers now choose convenience and technology over anything else. Huge investments made into restaurant infrastructure are bringing back zero ROIs. All efforts are going into breaking even for the investment into technology platforms.
Considering problems are expected when evolution happens, this whitepaper has made an effort to study areas that need special attention while developing a platform for online food services. Before entering into the food provider category, a wise analysis of the situation at hand will help devise strategic plans to manage platform operations and revenue as a business owner.
The discussion ahead will possibly help align resources and technological assets in the right direction for aspiring foodpreneurs.
i. Integrating third-party Delivery Services
The decision to set up an online food ordering and delivery business is without a doubt one of the most successful ideas in today’s times. An ever increasing demand and technology developments have favored the line of business.
When the need is to launch online food services, similar to the ones already playing in the market, spending time on building all the features and training the staff in-house for different roles might be unnecessary efforts.
Various established brands render their services, which the admins or owners can buy or outsource, either through APIs or direct services respectively.
Delivery partners provide professional services where the delivery, and sometimes even the platform, is managed by the third-party. They offer to complete all orders that pour in for the restaurants registered on their app. Right from providing an online channel, to marketing for the restau→rants, to assigning orders to the delivery staff, and arranging order tracking, a major chunk of the work is shared between the delivery partner and the restaurant.
- How then does third-party service integration present as a challenge?
- When a restaurant registers on an online platform to avail home delivery services for its customers, it pays a subscription fee or sign-up amount to the delivery partner.
- Every order completed is at times charged with some commission from the restaurant. Some delivery partners are charging upto 30% of each order amount.
- These amounts pile up and add to the financial burden on restaurant owners who set up their business on thin margins or are fresh into the business.
- Instances have been reported where delivery service partners charge for every call or request a restaurant receives, even if it does not convert into an actual sale, tends to build unnecessary and unjustified expenditures.
- In addition to paying a margin of their order amount for its delivery, restaurants have even had to add to their staff for packing of orders to be picked up by delivery personnel.
- All this despite the majority of orders still falling directly into the restaurant’s direct ordering pool, with only 22% orders being placed through third-party websites.
In times when home delivery services became indispensable, restaurants suffered huge losses trying to offer their menus at affordable prices due to increasing competition. Paying additionally to the third-party services to keep up with the increasing delivery demand added to their expanding investments being made on bleak margins.
- How to address this?
With online delivery now a mainstay in the food business, restaurants can re-think on the ROI towards this feature addition. Outsourced delivery, if developed in-house, can help restaurants save on the additional 30% of their business share invested only on commissions and subscriptions.
Developing a delivery arm for a food business and managing its online operations requires some basic requisites that will establish an end-to-end online food ordering and delivery value chain.
- Tools and Technologies – Establishing an all-in-all online food business today is a result of harnessing technology in the best of its forms. Technology service providers have been smart in understanding the market scenario. Software solutions that enable food business owners with an online channel for ordering as well as delivery management are available with all basic functionalities.
A robust software backed with good server support and a well mapped network connectivity developed between various modules of the online delivery architecture will establish a responsive service supplementing a good food business model.
- Staff Members – Dependable staff headed by a delivery manager supervising the software and operations, supplemented by good drivers that facilitate package drop-offs to the customers, are enough resources for basic delivery services desired of a food business.
- Operational Overheads – Inputs to functionalize logistics with delivery vehicles, packaging, storage space, and insurance formalities will mobilize the developed system. Every input required to augment the software as well as the resources will add to the completeness of a complete online food chain.
Calculating these investments in the longer-run will bring better returns and will add to the scope of expansion for the food business owners. The flexibility to scale and improvise business with in-house developed value adds will help the food business expand.
As all components of the online food ordering and delivery chain strategically fall under a single owner, maintaining uniform quality standards for better consumer experience will become systematically easier.
ii. The ever evolving consumer
Evolutions and revolutions since ancient times have led to changing dynamics. Most of these resulted in evolved processes, industries, and even entire communities. The food industry for one, has witnessed drastic developments and improvisations with changing times.
The consumer being the focus, around which food delivery services are designed, has been the most frequently evolving species amidst any value chain. Consumer preferences and demands lay down the rules for building better features within a food business model. When the demand was high for convenient dine-ins and table bookings, technological solutions like restaurant websites and applications came forth facilitating e-bookings for restaurant tables.
Not only booking tables vaguely, customers are now able to visualize the entire seating arrangement inside a restaurant, and choose from the available vacant tables for specific choices. Slowly, orders were being placed through restaurant apps simultaneously while dining in.
Such developments ensured that innovations are not alien to the food sector, and that something as simple as restaurant dining can be made tech-smart. Home deliveries took customer convenience a step-ahead, and apps were developed that brought almost all restaurant operations online.
From bookings, to ordering, to tracking orders, and leaving feedback, customers are able to enjoy fully-cooked meals from the restaurant kitchens straight onto their dining tables.
With every change, every new value addition to the process of cooked meal dispensing, and changing times, the consumer evolved, and so did their preferences. What began as adjusting to digital revolution and survival tactics, are now being expected as regular practices.
Demands for sophisticated technology backed processes pushed food business owners to test their resilience throughout the pandemic. Despite being at the limits of their business revenues, they brought to function every trend to satisfy their customers.
Among various challenges that engulf the online food industry, frequently changing consumer behavior and preferences has been a daunting one to address. All being done and implemented to meet the consumer choices, the new and trending has always been able to grab the attention.
The volatile nature of loyalty towards food taste as well as attractive technology-backed means of selling, has left the consumer switching between choices, posing a new benchmark for the restaurateurs every now and then.
- Prominent reasons for evolving customer behavior and patterns
- International entrants into local markets have raised the threshold for small restaurants to provide more in less, raising the bar or expectations for everyone to perform.
- Recession by the pandemic has left consumers choosing affordable options available. Switching from their regular supplier to newer ones offering better discounts in return of loyalty become easy choices.
- Being forced to stay at home, exploring new apps with newer ways of delivery, variety in cuisines, and discount deals, seems like the only change they are making in their otherwise limited schedules.
- The transition from offline to online dining was more of need-of-the-hour amid the COVID spread, but the convenience seemed to set well. Especially where dine-in restaurants charged more for distinguished services compared to fast-food or takeaways, job and income cuts made the shift almost permanent.
- Convenience has guided them more than anything. Intelligent business models and apps, using consumer behavior history, have enabled consumers spend less time in making decisions. Prompt and responsive interfaces through mobile devices are definite attractions, leading to easy switching between online food ordering and delivery platforms.
The struggle for online food business owners seems never ending in this picture. Restaurateurs should prepare for long lasting and viable solutions that enable flexibility and scalability in their online food ordering and delivery systems. It is certain that drawing assumptions on consumer behavior and preparing to meet them in their customer journeys with mindful solutions has helped food businesses sustain even during the toughest of times.
- Addressing the Challenges of Evolving Consumer Behaviour
The immediate improvisations to online food models and delivery by many established brands have proven that strategically planned steps helped them retain customers. An attempt towards including provisions into their online food ordering and delivery software at the time of integration or development can make a huge difference.
- Know your Customer
- Understanding the audience or the consumer better so as to decipher how they will adapt with changing times, or adopt anything new.
- The key to knowing the customer better is by gathering even more information about them, their behavior, choices, and response to any change.
- Adopting technologically advanced approaches as part of the software to retain the data points significant in regard to customer behavior and choice:
- Capturing information related to customer demographics at the time of registration on the platform or application will help link their choices based on age, gender, and location.
- Using the order history of an individual will certainly help investing towards more popular items, price them accordingly, as well as giving recommendations as they visit the platform again.
- Reviews and feedback can be analysed to better understand the popularity and lacunae within the existing offerings
- Every activity of the user on the food platform needs to be captured as a data point and saved in a database, securely maintained. The owners must define formats for storing or capturing information.
- Online platforms or software need to be developed with or integrated with databases at the backend, prepped with codes for all structured as well as unstructured data to be saved numerically.
- Secure and stable databases could offer huge benefits to the online food platform owner. Invest into a POS (point of sale) and a CRM (customer relationship management) database.
- Integrating Data and Analytics
- Pulling data from across the online food platform, from the multiple data sources like the POS, CRM, menu analytics, and guest analysis will be the ultimate source of in-depth understanding that can be gained.
- Integrating powerful and customizable business intelligence (BI) platforms that manage the integrations, data catalogs, data lineage, plug-ins, different sandboxes, and tools for a complete data infrastructure along with analytical reports or scorecards.
- These understandable outcomes of the analytics software will provide better understanding between different variables, enabling the owner to draw meaningful insights for the present and the future.
- Descriptive, predictive, and preventive analysis will help take key decisions that will retain customers to sustain the online food ordering and delivery business across situational variations.
- Optimising Operations in-line with Analytical Outcomes
- The most significant factors that impacted popularity and sustenance of any online food ordering and delivery platform from a customer’s point of view are:
- Speed of delivery
- Payment options
- Quality of service
- Time saving
- When important inferences will be drawn from customer behavior, ordering pattern, likes, and feedback, the business can concentrate on maintaining standards with respect to all these parameters.
- The idea should be to give back in return for the valuable data that the restaurants or business owners get from their customers.
- If data points are captured in full transparency and in agreement of the app or platform users, with value driven returns through better services offered, there is definite possibility of enhanced loyalty.
- The most significant factors that impacted popularity and sustenance of any online food ordering and delivery platform from a customer’s point of view are:
The uncertainty related to how the consumer will behave or adapt with changing times can be minimized with properly planned platform integrations and development. A lot can be significantly controlled by harnessing and evaluating platform data, for more value to the online food services, in turn improved business outcomes.
iii. Food and Labor Costs
The online food industry is an ecosystem which functions on the efficient coordination between a software and a team of members taking care of the different steps involved in delivering fully cooked meals to the customer’s location.
Convenience delivered along with food via online channels is making a majority of customers shift to this way of dining. It is however noteworthy that every convenience has a price. Be it the consumer, the restaurant owner, or the delivery staff, each one contributes a fair share of their revenues for the success of an online food delivery process.
As challenges pose limitations towards the seamless functions, piling costs add up to the pressure building over the food business owners. Operating an online food delivery business requires key inputs from various sources and resources, which actually contribute to the cost of the item being cooked and delivered.
While dealing with challenges related to fluctuating consumer choices and third party tie-ups, the restaurant or business owner is simultaneously busy accounting the costs going into running the online channel. Despite choosing to execute an online arm of the business for better profits, understanding where the investments drain is of significant importance so as to manage the overall finances.
The online food business is actually functional when the static and mobile services work hand-in-hand. What goes in does come out in certain percentages, and needs to be controlled to some extent for better ROIs. Calculating cost of deliveries allows a better insight into the different kinds of costs that play a part in delivering food items. So, the delivery costs can be broken down as:
Cost of Delivery = (Fixed costs) + (No. of Deliveries * Variable costs)
Figuring out the fixed and variable costs descriptively impact how a business owner is able to manage this cost. The fixed costs include expenditures like bearing insurance, advertising, an integrated connection or service provider, software or website, sustaining the kitchen staff, and material procured for packaging and delivery. Basically costs which are concentrated towards the basic online business processes fall into the fixed cost category.
Predictable, unavoidable and recurring, the fixed costs if compromised on will end up degrading quality of the online business as well as pose roadblocks in the otherwise running chain of events.
The variable costs are expenditures on vehicles for delivery along with all costs that go into maintaining them, driver wages, and the bank charges for online transactions. However, a number of factors influence their unpredictability and dependency on external market uncertainties.
A major chunk of the variable costs is built on the inputs towards the vehicles being used for completing online orders. A detailed estimation towards these expenditures can help with better financial planning and directing the sources wisely.
When charging a consumer, these costs are placed under different heads of the food bill so as to break even. So, there is a menu price of the food item visible to the consumer online, and then various other charges added at the time of payment by the merchandise. To get back some percentage of what goes into cooking, connecting online, and delivering the meal, the bill includes various fees:
- Item Menu Price
- Fees and taxes
- Service fee – charged by the delivery partner or for the delivery arm
- Tax – sales tax as per local tax laws
- Delivery fee – for home delivery
- Gratuity – the optional tip to the driver
Having bifurcated these costs and prices, the challenge for the restaurateur arises when all these are sorted on paper, but not in accounts. When the business owner starts providing services a number of new joinee offers and deals are offered, discounts are run on the platform, and many free deliveries are done based on many factors.
A number of additional features on top of these costs, which cannot be billed to the consumer, are run on the online channel for marketing, and advertising purposes.
- Including personalization
- Multi-location ordering
- Specific insulated packaging for seasonal deliveries
- Eco-friendly packaging as new options for saving on costs
- Premium offers on certain food items
- Rewards on different platforms
There are many technology-forward platforms that have emerged lately, which run marketing campaigns, and have been able to manipulate market demands, tipping the scales with respect to desired costs. In order to sustain amidst the hefty inputs desired, the online food business owners now need to be strategic in their investments.
Addressing the stress that precipitates due to these costs, especially those that delineate from the planned investments, a well synchronized approach towards business operations has come out with benefits. Better managed costs towards the food as well as resources can happen if proper steps are taken.
- Technology is the Key
Understanding the way the world is changing everyday helps realise the pace to be kept in order to stay at par. Food businesses grabbed every opportunity to bring that change and become what they are today. Superfast deliveries with an extensive network, spreading online food services in almost all parts of the world.
Harnessing the benefits of technology brought online food business to a place today where convenience is the primary deliverable. It is technology and the solutions developed that propose to unbundle most of the cost issues disturbing owners of online food channels.
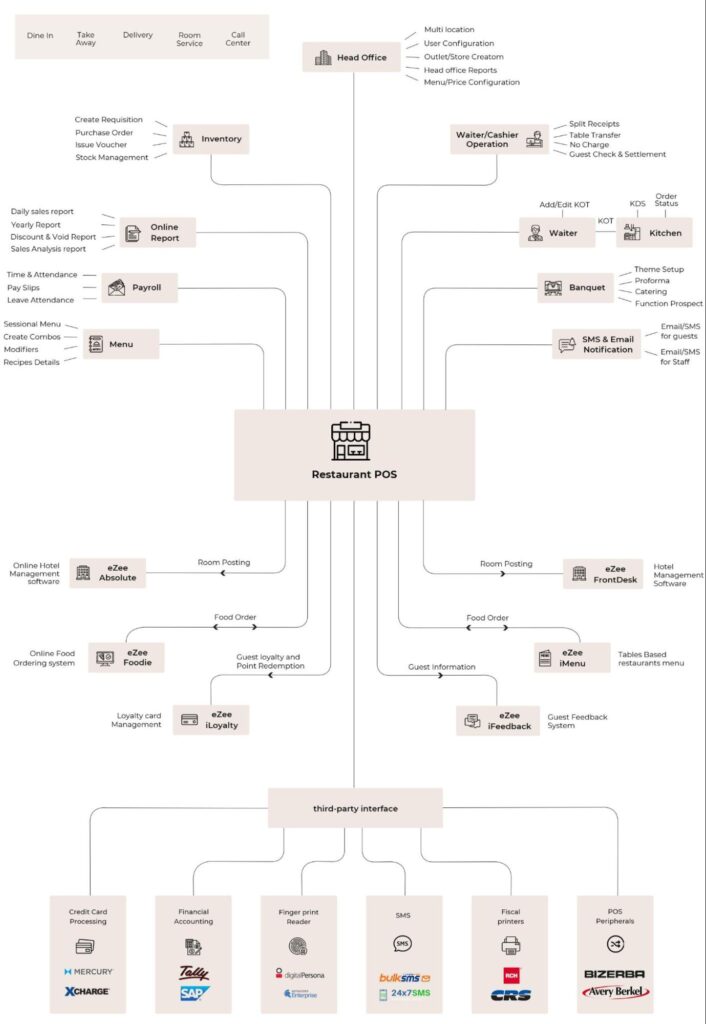
Focus towards technology-centric methods of calculating the profit margins, using standard methods to calculate the food costs. Smart software to design menus with POS software or applications for sales and inventory management help reducing errors, in turn improving efficiency. Integrating a robust POS will help solve many of the challenges being faced due to everyday events and additional costs that accompany.
Then there are technology offerings like Kitchen Display Systems (KDS) that automatically pick up orders from the POS and speed up the connectivity between different resource groups on an online food ordering and delivery value chain.
Adding customer management tools to the online platform will enhance engagement and improve customer relationships. With software automating the recurring tasks, there will be time for enhancing business on various fronts.
Menu management with the help of software tools that provide a detailed analysis of popular items versus those selling in groups can contribute in designing better menu structures. Decisions like grouping certain items together, placing bestsellers on priority with highlighting items of the day, introducing different offers, pricing popular and unpopular items accordingly, will be definite positives in saving at a lot many places.
- Percentage of Food Cost – Define it
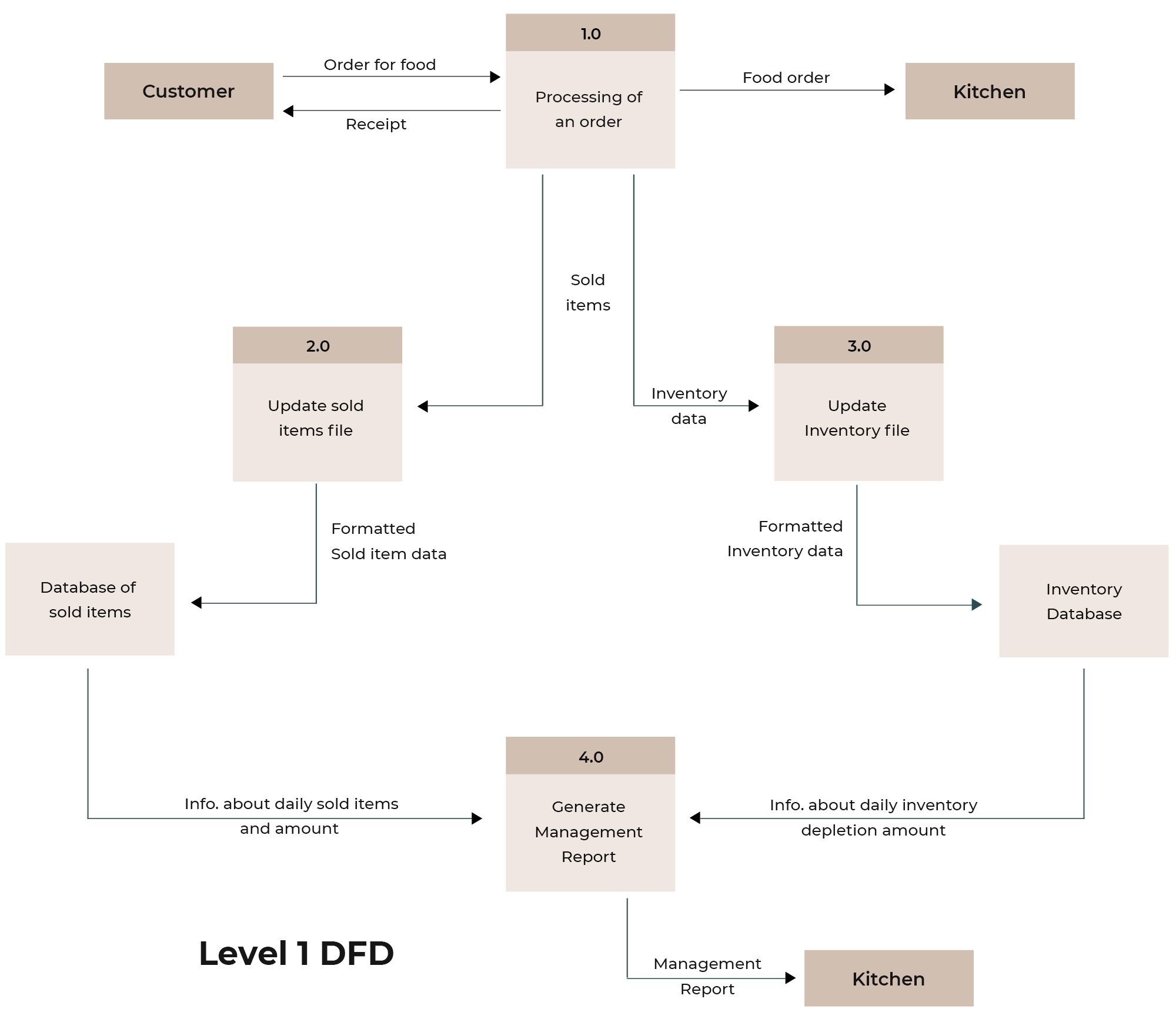
To begin with, be certain as to what percentage of the total cost is being consumed by food alone. Bring into consideration the cost of the sold products and the sales happening. Defining it mathematically:
(Cost of Goods Sold / Food Sales) x 100 = %age of food cost
Ideally, an online business should be investing somewhere between 25-35% on just the food. However, this could waver depending if the expenditures are less on the labor or infrastructure and rentals. Chalking out the figures, and keeping them within the healthy limits will help contain unnecessary wandering into stressful zones.
Being specific in portion sizes also plays a part in the food cost. Through proper analysis of data related to reviews, customer feedback, and wastage, the order sizes or portions delivered to the consumer can be modulated per dish. This will contribute to bringing down much of the excess costs and controlling the overall food cost percentage.
- Inventory and Purchase Management
Again, a well planned and executed management with the help of software tools integrated into the online platform will play the main role in bringing down unexpected food as well as labor costs.
Purchasing in-time as per demand assessed via order analysis will help prevent unnecessary pile up of inventory and food wastage. Waste food material is a major reason for high food costs being borne by online food chains. Get bulk raw food material directly from the providers, instead of buying through middle-men.
Register on the platform farmers and providers who can supply according to inventory demand being generated online. When such trades happen online, the possibility of errors happening are reduced.
Enlisting quality standards as well as quantitative requirements on the portal for suppliers to gain clarity minimizes chances of unwanted buying, ultimately, positively affecting finances of the online chain.
There are communities and organizations of online food ordering and delivery services that together place bulk purchase orders to providers, trying to save on small size ordering. Staying connected to these communities has really done a lot much for the struggling online food delivery business owners.
- Staff Optimization
Utilizing technology to its maximum capacity can help manage the challenge of high labor costs too. Scheduler tools and shift management APIs should be integrated into the online platform to coordinate an efficient work environment.
Try getting on-board cross-trained staff where each one can be assigned multiple tasks as per availability and need. Unnecessary waiting of idle drivers or cooks at the time of low orders, and then their unavailability at the time of peak orders will obviously imbalance the entire chain.
The scheduling tools will clearly analyse the total involvement and working hours of each employee registered on the platform, and assign relevant tasks appropriately distributed as per their working hours.
Shift management software will automatically let each member know when they need to handle which duty and hence an efficient online food delivery platform will be the outcome.
Route optimization software or APIs as part of the online food delivery platforms must become essential in order to help save substantially on the drivers’ efficiency. The tool organizes and clubs orders from a single location or falling on the same route. This will prevent all resource utilization into a single direction, plus will help drive more ROI out of the deliveries.
Apart from these solutions, generic approaches to offer a different e-menu everyday with daily specials according to food that came in stock earlier and are close to their expiry, serving seasonal items, and donating extra food, will do a lot in justifying as well as nullifying additional costs that present as a challenge.
iv. Regulations over Food Delivery
The idea of online food ordering as well as organising processes for home delivery of these orders have presented as attractive business opportunities to those who have wanted to own food businesses. Infact, options in regard to business models in the food industry have gone up with the recent pandemic and new ways in which consumers are ready to reach out to cooked meals.
More and more activities happen online, with a reduced human intervention, and with lesser scope of variations, as expected in manual procedures. The food system traversed from offline to online with such a rapid pace, that clear, distinctive, and globally uniform guidelines for the online versions barely came through.
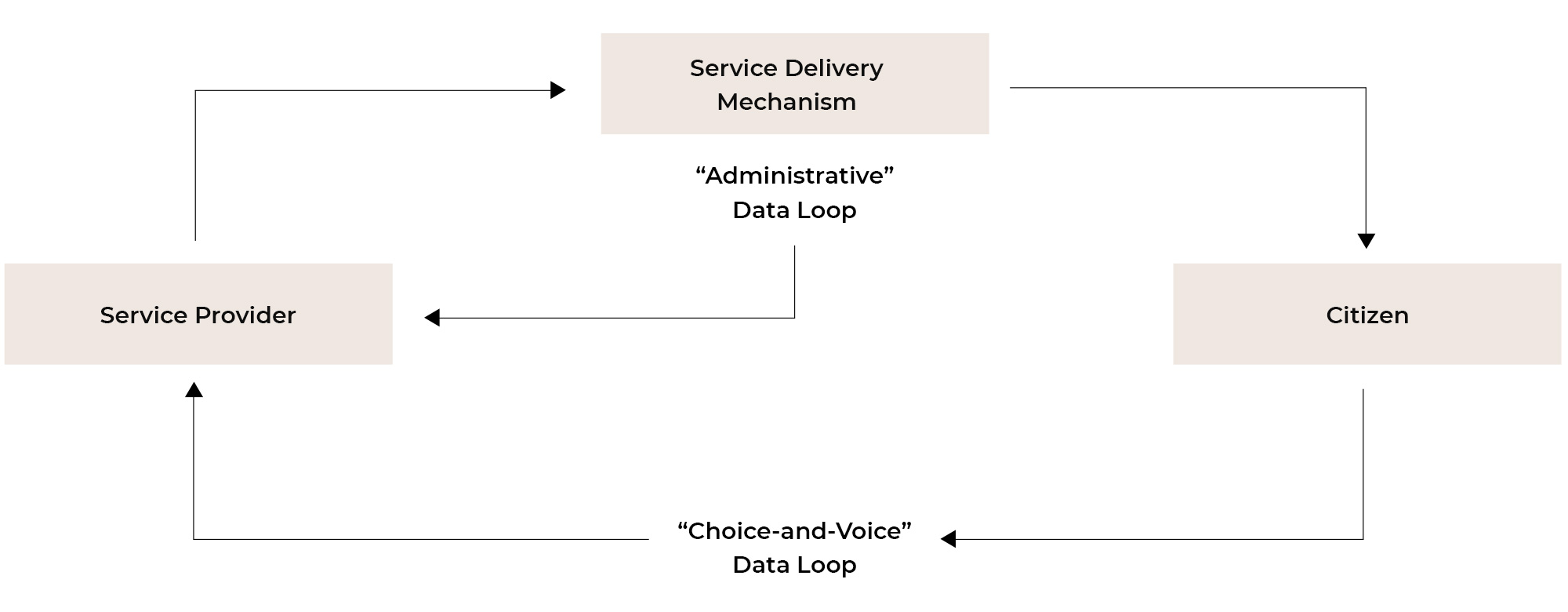
Also, due to a variety of models in function, laying down rules and limits for each one is a task that needs to be thoroughly addressed. It so happens that within the online food ecosystem, delivery operations can broadly be categorized as direct-to-consumer (DTC) and third-party delivery (TPD). From this point of view, the delivery module management is one of the key differentiators when deciding on who takes the responsibility for what reaches the end consumer.
The idea behind food delivery services, restaurants, retailers, third party delivery companies, seeking defined laws and regulations is to primarily protect their own interests, employees, and reputation. The regulations ultimately help them serve better, and in favor of their customers’ health.
The US-FDA and the CDC (Center for Disease Control and Prevention) did lay down best practices for food pick-up and delivery, especially during the COVID-19 situation. Some statements on managing meal kits and delivering them safely came as a help to the food delivery parties. Whereas there are special instructions like checking the packaging seal, examining the box, and temperature of the food if above 40 degrees Fahrenheit, out for the customers too.
Still, with just a few guidelines, on condition and quality, restaurants migrated to online channels with the existing regulations for restaurants. This is where the problem began. Questions like:
- What regulations to follow – state or national?
- Who is responsible for risk management between the restaurant and delivery team?
- How to ascertain if the steps being followed are legal and within compliances?
- What are the allowed formats for consumer communication?
- What are the best practices for a DTC service and TPD services?
Such dilemmas pose challenges for the online food delivery service offering companies, restaurants, as well as the public health authorities. Absence of strict guidelines for both the DTC and TPD services, regarding procedural controls, risk assessment, process validation, verification procedures, instructions for packaging, storage, physical or chemical contamination control, and procedure recommendations for return of soiled or compromised items delivered, leave them questioning authorities.
Not only this, the countless reviews and feedback on substandard deliveries and low quality products being used to prepare meals, are only being answered on a case-to-case basis. There is otherwise no process being defined on a large scale that can be applied to all uniformly across the online food ordering and delivery industry.
The rift between the central government rules and the state laws is one of the key reasons for this challenge to pile up on those completing the orders.
Addressing this is becoming increasingly important, more so when online channels are becoming the mainstay, even so for cooked food delivery. In order to maintain quality, safety of consumers, as well as define best practices to standardize the process and procedures globally, regulations need to be in place.
Having been said so, strict regulations are still considered as a scourge and a hindering parameter to a company’s profitability. However, it must be noted that regulatory fragmentation can be seriously outweighed if these laws and standards are imposed efficiently.
- Implement Checks Online
Authorities are gearing up, sharing descriptively the instructions on processes, to keep all parties aligned with respect to maintaining standards. The foodpreneurs and restaurateurs functioning primarily through online channels, however need to realise that maintenance of basic quality standards through random system checks keeps good practices in place.
The advantage of operating through an online platform or application is that supervision can be automated. Making regular entries, and penalising the ones missing on their entry with every order can help maintain regularity and data quality. Once in a while, the data can be cross checked with actual values to validate the process.
The software can be programmed to raise an alarm if temperature, delivery time, and other values are found deviating from promised standards. The data flow within the software can regulate where prompts need to be placed for making entries
With detailed reports being generated, spotting outliers will be easy, and the pile up of erroneous steps can be easily handled at the individual business level. The online food business owners will be able to manage better, report better, and upgrade better. Technology will serve the purpose of supervision at all levels and at all times, without any additional resource on the team.
- Share Feedback and Review Data with Authorities
The major advantage of setting up an online business is that despite being distant from the consumer, the feedback and reviews keep collecting. To bring the best use of these is to collect them systematically in a database and analyze them to understand scope of improvement.
The challenge faced due to unavailable directions from food and regulatory authorities can be conveniently addressed by helping them understand the lacunae better. When they will be able to assess the reviews and problems faced by consumers on a regular basis, laying down ground rules will become a necessity.
As suggested by members of the food council that they are unable to define set rules for the DTC and the TPD services as they fail to understand the areas of need, access to consumer feedback will be a definite direction. While developing modules for mobile access, it should be inbuilt that the reviews regarding logistic or operational parameters be summarized as a report that can be shared with the regulatory authorities.
With a regular update on the areas that need attention, from every online food service provider, the burden of defining standards can be shared amongst the business owners and the authorities. They can work jointly to design jurisdiction with regard to online deliveries and services of food.
- Identifying Problem Areas
Identifying the need to maintain these records, share them on a timely basis with regulatory bodies will facilitate better guidelines for the online food delivery industry.
Observing the delays or issues with less drivers will help highlight the issue of driver rights along with guidance on the restaurant-to-consumer and third-party delivery processes.
The online platforms can help statistically visualize the repetitive reasons for delays in delivery. Details of drivers lodged into the system will showcase how many need to be provided a proper employment status so as to serve uninterrupted.
Collaborating all the online data at hand with those who can play a major role in refining these services will contribute immensely to solving the challenge of undefined regulations. The future thus demands the two, food service providers as well as rule makers to come together, make the best use of technological tools available to enhance the online food sector.
iv. Increasing Competition
In the process of delivering for the evolving market demands, almost all food businesses have migrated to online versions. Transitioning the business and operating it through an omnichannel has become the new way of retaining customers.
Since everybody is upto endorsing technology offered solutions to provide more convenience and better services, the customers are finding it hard to remain loyal to any one in particular. Changing trends and consumer behavior has invited many to venture into this direction on offering online food delivery services. More and more online food business models have made it increasingly difficult for the existing ones in many ways.
When a foodpreneur finalises on a business model, investments are made in the direction of facilitating all requirements for the same. Time, money, and efforts to initialize the operational flow take impact when a competitive business starts offering more in the same price. For a simple reason of winning customers, compromises are made on many fronts.
The problem is primarily when these competing businesses are multinational chains, established market names, and can afford to offer the same in less. Whereas, local online food vendors are not able to draw even with such prices and offerings. Although unavoidable, certain steps can definitely help surpass the pressures of an ever increasing competition.
- Market research
It seems market research has become more of a routine instead of a high priority. Prospective business owners either do a superficial analysis of the market themselves, or hire a part-time third-party to conduct a local market survey. It rather needs to be one of the primary and most desirable steps when beginning an online food delivery business.
The way to beat upcoming competition is to identify what specific the market demands, and whether you are filling that gap. The approach can be defined based on the vision. Identify the target audience for your food niche or cuisine. Try reaching them in a targeted manner through the platform instead of the entire user base.
Also, identify unexplored markets and hyper-locations along with the available food delivery options in these areas. Study in detail, through the online platforms visible in the hyper-localities for their menus and frequent orders. Their recommended items can indicate the local choice, and the reviews on their platforms can describe the expectations they have from cooked food delivered.
Observations on consumer demographics, drivers, order frequency, and density according to different areas can help fill a lot of existing gaps. So, the idea is to conduct detailed market analysis of online platforms before beginning to offer anything at compromised prices to simply win customers. Strategic business decisions backed with strong analysis of the market dynamics around can make a big difference.
- Competitive Platform
Technology is agreeably going to be the most attractive of all business interventions. With enough emphasis put on the quality of food and variety of options to choose from, unless the online platform is able to put across an edge, customers will fail to reach the order button.
Developing an online food ordering and delivery platform today is even more intriguing than designing a whole restaurant. Every investment made is going to pay, depending on the ease of online ordering provided. Development should focus on the consumer, and be progressive, so as to be able to implement new changes with regard to technology.
With basic features like sign-up, paying online, tracking orders, interactive push notifications, smart bots, easy and variable payment methods adding to convenience in every way, the consumer is made well accustomed to demand for more. The concept of making it competitive must include deciphering how the competitor platform will evolve.
Decoding capabilities of the competitor online food ordering and delivery modules to grow with changing trends can help in an advanced development approach today. Understand better what marketing strategies and approaches are working for their visitors so as to design better campaigns.
The trend of smart platforms that assist the platform visitor with suggestions on dishes by understanding their ordering behavior will always stand ahead. Audio in-app suggestions and navigation can make the platform interactive and a sense of ordering along with someone can be highly engaging.
A server and network support that ensures an uninterrupted experience without mid-process crashes and delayed updates while ordering food online is always bound to offer a competitive advantage. Saving the consumer’s time and delivering their favorite food within the promised estimate will end up improving platform business.
- Drivers and Delivery Management
Business within an ever changing ecosystem is a challenge everyday. The online food ordering and delivery industry is constantly evolving and growing in all aspects. Delivering against a competitive landscape gives the business owners an inspiration to keep on their toes.
The last mile or order completion leaves a lasting impression in the minds of the consumer. A streamlined delivery will play an important role in checking all boxes related to a competitive edge generation. Ready availability of drivers is the primary prerequisite for an efficient last mile delivery.
The point is getting smart with the help of technological tools. Platforms do offer certain facilities of driver allocation, route optimization, delivery tracking, push notifications, all inclined towards improving delivery of food, but the point is to gain an edge amidst the crowded market.
- Investing towards developing an intelligent driver app to supplement the online food platform will provide a definite benefit in gaining positive customer reviews.
- Smart driver apps that manage schedules as well as suggest routes to drivers in sync to the upcoming orders will keep them prepped well in time. Driver scheduling tools for efficient fleet management will automate the process and reduce any chances of overlays or delays.
- In-app calling as part of the customer and driver apps will contribute to providing freedom to the customer to contact their delivery person. This will allow a direct bridge between the consumer and driver, thus providing a comfortable ordering experience.
- The data pertaining to drivers and deliveries must be managed with a stellar database system. The business owner must be able to analyse driver data so as to make decisions that improve platform performance with regard to best utilization of available resources.
- There need to be temperature logs inbuilt in the app or platform where the drivers as well as consumers can log in the temperature of food items while delivering and on delivery. The log database can be kept as a reference for improving services as well as implementing regulatory checks on the food delivery.
The key to keeping ahead in the game of engaging customers on the food ordering platform is to be a step ahead of the competition. But simply doing something different will only end up burning the owner’s pockets. Strategise moves to fill gaps within the existing ecosystem. Offer to the consumer what the others are not able to even with heavy investments. Embracing technology in the right places and to the right extent will always contribute to a balance between investments made and benefits drawn.
Visit white paper Volume 4 for further details on food delivery business market.

